A couple of days ago, Fedora 12 was released on the Internet. We downloaded the x86_64 (64-bit) version of the distribution to check it out. Once more, we installed the distribution in a virtual machine created using VMware Fusion 3 running on a 2.4 GHz MacBook with 4 GB of RAM.
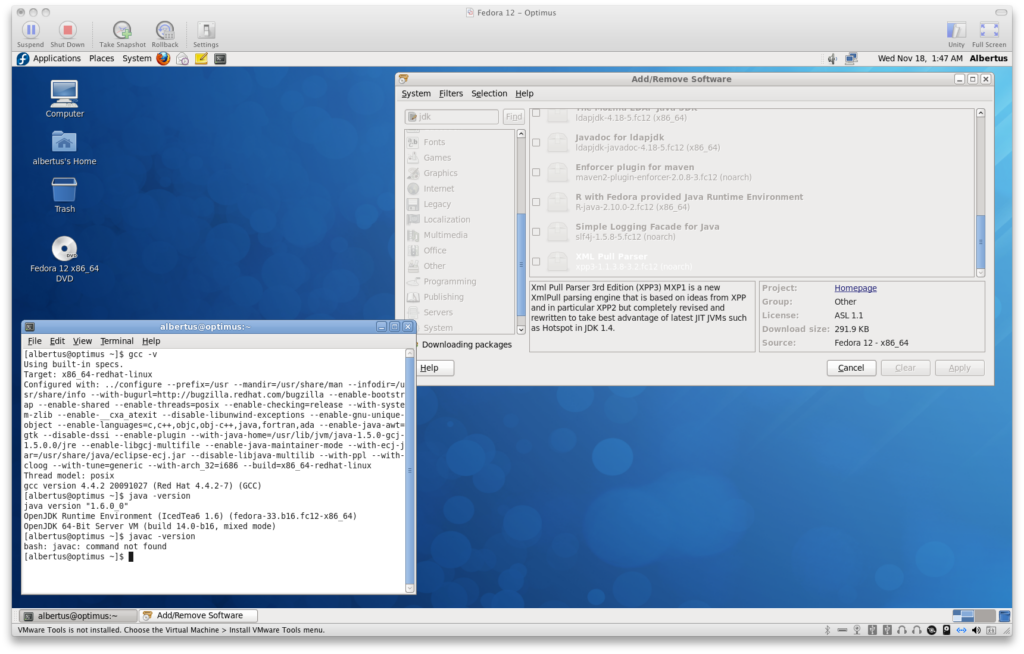
A disc file image of Fedora 12 was used to install the distribution on the virtual machine. Installation was speedy.  Aside from the default selection of packages, we chose to add more development tools to allow us to compile other programs manually. We also added the OpenJDK development package after the install was done and after rebooting into the new system.
Aside from the default selection of packages, we chose to add more development tools to allow us to compile other programs manually. We also added the OpenJDK development package after the install was done and after rebooting into the new system.
The default screen resolution was 800×600 pixels. This was chosen probably because it was a safe setting for the video driver (vmware) selected. However, we decided to increase the resolution to 1680×960 pixels by modifying /etc/X11/xorg.conf. Like what we did with OpenSUSE 11.2, we added the line:
Virtual 1680 960
The steps to do this were the same. First, put Fedora 12 to run level 3 (without X running). Then, execute ‘Xorg -configure‘ to generate an xorg.conf file in root’s home directory. Copy this new configuration file to /etc/X11/xorg.conf and edit the new file by adding the Virtual line above. Run X using the command ‘startx‘ to see if the configuration works. If it does, return to run level 5 to bring up the desktop login manager.
The login screen of Fedora is quite simple. It uses the Gnome Desktop login manager:
The default desktop is Gnome although you can get different “spins” of Fedora with KDE and other desktops as defaults. Below are samples of the desktop running programs including Java applets courtesy of OpenJDK.
We also got a Logitech Quickcam Pro 9000 webcam to work out-of-the-box with Fedora 12. We first had to tell VMware to attach the device for Fedora to see it.
Some Java apps running using OpenJDK. Note that the OpenJDK installation in this VM is 64-bit.
For now, that’s what we have on Fedora 12. We’ll be back with more Linux articles.